Vehicle to House - EV Battery Powering Your House
by drmpf in Circuits > Gadgets
142 Views, 1 Favorites, 0 Comments
Vehicle to House - EV Battery Powering Your House

Update 7th March 2026 – Changed relay from 30A to 60A and added RC coil suppression.
This project connects the EV (Electric Vehicle) car battery to the house to power it during blackouts or more commonly to avoid using high cost electricity, i.e. load shifting. This project requires the assistance of a qualified electrician to add the power wiring and modify the switch board.
The cheapest storage you can get is your electric hot water tank. A typical electric hot water tank stores more than 10kWh of power as hot water. See HotWater from Excess Solar V2 or there are commercial solutions for less then AU$1,000 (plus installation). Search for “solar hot water timers controllers”
For battery storage to power your house during blackouts or during peak electricity price period, EV's provide the cheapest battery storage in $/kWh and you get a car as well. For example, in Australia, an Hyundai Inster Extended Range (~AU$43,000 drive away, Dec 2025) is ~AU$877 / kWh (and there are also other cheaper Chinese cars to choose from), while a Tesla Powerwall 3 (~AU$12,400) costs ~AU$920 / kWh after a 30% federal rebate!!
To power the house from the car, the extra parts and installation by an electrician was less then AU$1,500.
This project is also online at Vehicle to House
Supplies
1 x Electric Vehicle with 3.6kW of V2L capability, i.e. Hyundai Inster ~AU$40,000 42kWh battery to ~AU$43,000 49kWh battery.
Note not all EV's have V2L connections and some EV's only provide 2.2kW of output which is not sufficient to power the house.
1 x Hyundai V2L connector AU$595. There are third party V2L connectors for less than half this cost.
1 x 63A rotary switch, e.g. YAMING YMW26 63 from Aliexpress ~AU$25.00
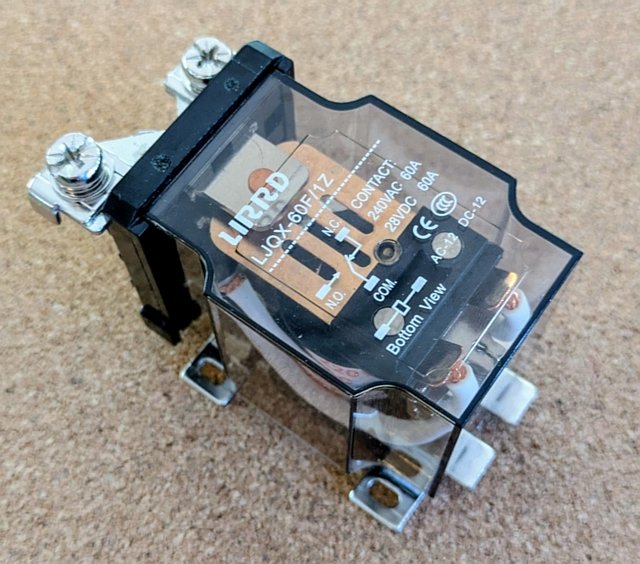
1 x 60A 240V coil relay SPDT, e.g. LIRRD LJQX-60F/1Z from Aliexpress ~AU$14.40
1 x 1R0 1/4W resistor, e.g. Jaycar RR1502 pack of 8 ~A$0.65
2 x 0.47uF 250VAC X2 Metallised Polypropylene, e.g. Jaycar RG5240 ~AU$7.50 OR 1 x 1uF 0.47uF 250VAC X2 Metallised Polypropylene, e.g. Jaycar RG5248 ~AU$4.25
1 x plastic box to mount relay in. e.g. AG-1212-S 125mm x 125mm x 75mm from Aliexpress ~AU$18.00
1 x 15A extension cord e.g. HPM 15m 15A extension cord ~AU$35.00
1 x extension cord connector cover, e.g. Arlec IP44 Outdoor Safety Box ~AU$4.00
Optionally for Desktop Computers – Cyberpower BR700ELCD UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) ~AU$280
KW Versus KWh
kW (kilowatts) is how fast power is used / supplied. kWh (kilowatt hours) is the amount of power used / available. Appliances have their power usage, kW, marked on their base. A kettle is typically 2kW. If you boil the kettle for 10mins you use 2kW x 10/60 hrs = 0.33kWh. Batteries have both kWh, how much they store, and kW, how fast they can supply power.
In this case the car battery has 49kWh of stored power but can only supply 3.6kW at a time. So if, for example, you turn on two kettles or a kettle and a 2kW radiator, the 4kW will exceed the how fast the V2L can supply the power and the car will automatically turn of the V2L output. This is why an EV is only as 2.2kW output is in-sufficient because your house will have lights, computers, TVs, and refrigerators running (say 0.4kW or more) and when you turn on a kettle of heater, the total will exceed 2.2kW and the car will shut down the V2L output.
In Australia, any appliances that plugs into a standard outlet will use less than 2.4kW. Led lights use only a few watts (0.005kW) each. TVs, usually less than 100W (0.1kW). Desktop computers, usually less than 100W (0.1kW). Laptops even less. Refrigerators use about 100W (0.1kW) when running, but draw a spike of power ~1.4kW when they turn on.
In this installation, the base house load is 600W to 700W (0.6kW to 0.7kW), which with a 3.6kW V2L supply allows for one large appliances to be used at a time i.e. a kettle, hot plate, room heater.
Circuit

As noted above, if the instantaneous power usage (kW) exceeds the capability of the car's V2L, the car will shut off the V2L for protection. The car will also turn off the V2L when the car battery reaches the minimum charge level set by the user, say 20%. To avoid loosing power to the house if either of these events happen, a change over relay is used to switch back to mains power if the V2L power disappears.
See the circuit above (pdf version)
When the 3 position rotary switch in on the V2L position, the 60A relay controls which power is supplied to the house. If the V2L circuit is active it energizes the relay and connects the V2L to the house. If the V2L supply turns off, the relay de-energizes and the house is supplied from the house battery (or mains if the house battery is flat). The RC series circuit damps the turn off voltage spike of the relay's coil.
To minimise the chance of exceed the V2L supply capability, only Selected House Circuits are connected to the V2L / Battery change over circuit. For example the oven would be be powered directly from the mains via House Circuits not backed up. Your electrician can help you sort out which ones should go where.
Construction
Most of the construction is undertaken by your electrician. Here is the Garage installation showing junction box, the orange extension cord connector cover and the V2L car plug in to which the extension cord is plugged.
The black section at the bottom of the V2L car plug opens to allow the extension cord to be plugged in.



The relay and RC suppressor circuit are mounted the plastic box.

Here is the rotary switch for the switch board


The rotary switch need configured as the three position switch shown in the circuit.
Connect contact 4 to contact 2 and contact 8 to contact 6, on the bottom of the switch, to from the Common connections for each pole shown in the circuit.
The switch terminals also need to be insulated to guard against fingers touching them.


Operation

In this installation, the house battery is used to soak up every little bit of solar production. Then the EV battery is charged from the house battery, which is then used to provide power when the house battery is exhausted. The house battery is used in preference because it can provide more than 5kW of supply. Enough for kettles and hotplates and heaters / air conditioners. The Air Conditioner is on the House Circuits not backed up.
When the car is powering the house the car's driver's screen shows the battery % remaining and in the bottom left corner the kW's being supplied by the car. In this case 2.1kW. The time remaining appears to refer to charging time, not discharging.
Desk Top Computers
Laptops have an internal battery so they are not effected by the transient loss of Mains when switching from Mains to V2L or back again. However desktop computers are more sensitive. Here we use CyberPower BR700ELCD UPS battery systems that keep the computers running when the power goes off. They also signal the computers that the power is off and will shut down the computer cleanly after a specified time.
Demand Pricing
There are a wide variety of electricity plans to choose from. A number of them are designed to encourage you to not use power during the peak evening period. On such plan has demand pricing (see Electricity Demand Charges). This plan has a relative low cost per kWh through out the day, but penalises you for power you use between 2pm and 9pm Monday to Friday. Demand charges can be very onerous because the maximum power usage on any one day is bill as though it happened every day of the month. See Electricity Demand Charges for the details of the calculation.
When it is running the battery control system feeds the battery back into the grid to offset the power being consumed by the A/C, but the solar battery is not large enough to run the A/C continually between 2pm and 9pm. On sunny summer days the solar generation runs the A/C until late in the afternoon and the battery handles it from then to 9pm. However on dull or winter days, the battery becomes exhausted. Using the V2L to power the basic house load of 0.6kW between 2pm and 9pm saves 0.6kW x 7hr = 4.2kWh from being drawn from the solar battery and so provide an additional 4.2kWh to run the A/C.
Having the fall back relay in the circuit means that if someone turns on the kettle and a hotplate at the same time and shuts down the V2L supply, the Mains / Solar Battery takes over with a slight flicker in the lights. Once that load has been sorted (when the kettle boils) you can go to the car and restart the V2L supply which will re-energise the relay and supply the Selected house circuits, in the mean time the solar battery supplies the power, so avoiding the demand load pricing.
On these dull days, the mains is used, prior to 2pm the fully charge the solar battery and to ensure sufficient charge in the EV's battery.
Power Outages
When there is a power outage, the solar battery takes over immediately to supply the Selected House Circuits, but its capacity is only about 8.3kWh and so well be exhausted after about 14hrs or less depending one the use of hot plates etc. On the other had the Hyundai Inster has ~39kWh available capacity (100% to 20% discharge) which can power the basic house load for about 2 ½ days. Together there is over 3 days of basic power for refrigerators, lights and boiling water and cooking. Also see the Main Off Detector project to alert you if the V2L supply switches off, for example while you are asleep.
Conclusion
This page covered using your EV's car battery to power your house. As well as the design and installation, it covered possible modes of operation to minimise your electricity cost and survive a 3 day power outage.